Bull Put Spread vs Bull Call Spread: Understanding the Differences for Successful Options Trading
When it comes to options trading, investors can utilize different spreads, such as vertical and horizontal spreads. This article focuses on understanding and comparing two specific vertical spreads – the bull call spread and the bull put spread.
Both strategies have defined risk and reward ratios, with the former being a debit strategy and the latter being a credit spread. Keep reading to learn more about the key differences between these two vertical spreads and how to make an informed decision for your options trading needs.
Understanding Bull Call Spreads
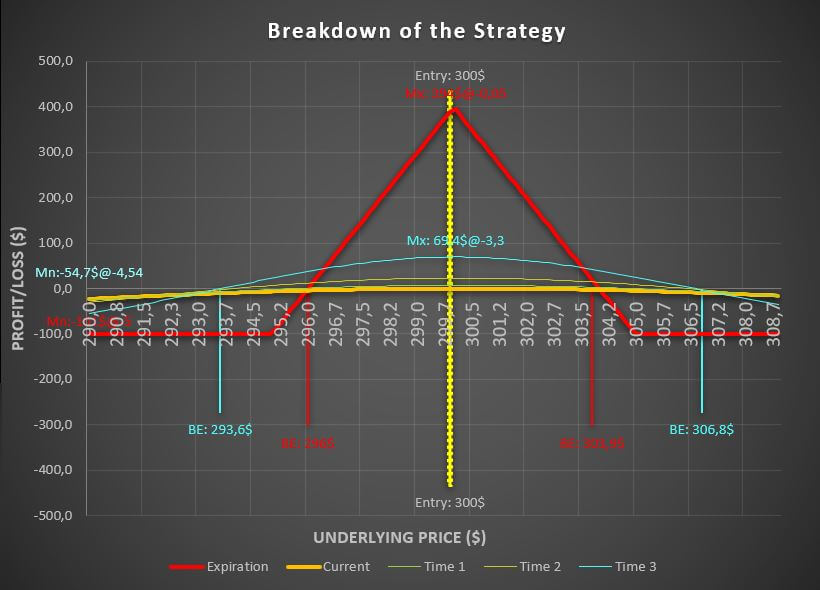
When it comes to options trading, a bull call spread is a vertical spread strategy that aims to profit from a bullish market by limiting potential losses. In a bull call spread, a trader purchases a call option at a specific strike price and simultaneously sells another call option with the same expiration date but at a higher strike price.
The goal of this strategy is to profit from the spread between the purchase price of the lower-strike call and the sale price of the higher-strike call, while also capping potential losses.
The Basics of a Bull Call Spread
At its core, a bull call spread involves buying and selling two call options with the same underlying asset but with different strike prices. The purchase of the lower-strike call acts as a way to “control” underlying shares at a lower cost, while the sale of the higher-strike call provides a way to generate income and hedge against potential losses.
This spread strategy limits the maximum profit and maximum loss of a single trade, making it a popular choice for traders who want to manage risk.
How Do Bull Call Spreads Work?
The objective of a bull call spread is to profit from a bullish market while minimizing potential losses. The trader buys an in-the-money (ITM) call option with a lower strike price and simultaneously sells an out-of-the-money (OTM) call option with a higher strike price, both with the same expiration date.
This reduces the capital requirement by allowing the trader to collect a premium for the sale of the OTM call while still benefiting from upward price movements of the underlying asset.
At expiration, if the stock price is below the lower strike price, both call options expire worthless. If the stock price is between the two strikes, the trader keeps the premium from selling the OTM call but realizes no additional gains.
If the stock price is above the higher strike price, the trader’s profit is capped at the difference between the two strike prices minus the initial cost of the spread.
How to Use a Bull Call Spread in Options Trading
One of the main benefits of a bull call spread is its ability to limit risk while still offering potential profit in a bullish market. This strategy can be particularly attractive for traders who want to take a less aggressive approach to options trading while still generating returns.
Some reasons to use a bull call spread include:
- To profit from a bullish market while minimizing risk
- To benefit from the spread between two call options with different strike prices
- To manage risk through capped losses and defined profit potential
- To generate income through the sale of an out-of-the-money call option
Example of a Bull Call Spread
Suppose a trader believes that XYZ stock will rise in the near future and wants to profit from this bullish prediction.
The current price of XYZ is $50, and the trader decides to enter a bull call spread by buying one call option at a strike price of $45 for $700 and selling one call option at a strike price of $55 for $300.
This creates a net debit of $400, which is the maximum loss the trader can incur in this strategy.
If XYZ trades above $55 at expiration, the trader makes a profit and the maximum possible profit is capped at $600. If the price is below $45 at expiration, the trader realizes a maximum loss of $400.
The Risk and Reward Profile of a Bull Call Spread
Like any trading strategy, a bull call spread has both potential risks and rewards. The risk and reward profile of a bull call spread is defined by the difference between the strike prices of the two call options, the net debit or credit of the spread, and the expiration date of the options.
This strategy has a limited maximum profit potential but also caps potential losses.
- Maximum profit potential: the maximum profit potential of a bull call spread is defined as the difference between the strike price of the two call options minus the net debit of the spread.
- Maximum loss potential: the maximum loss potential of a bull call spread is equal to the net debit of the spread.
- Breakeven point: the breakeven point of a bull call spread is the strike price of the lower call option plus the net debit of the spread.
It is important to note that although a bull call spread provides downside protection, it also limits potential gains.
As such, it is important to choose the right strike prices and expiration dates for the spread strategy, taking into account all relevant factors such as market conditions and potential changes in the underlying asset.
What is a Bull Put Spread?
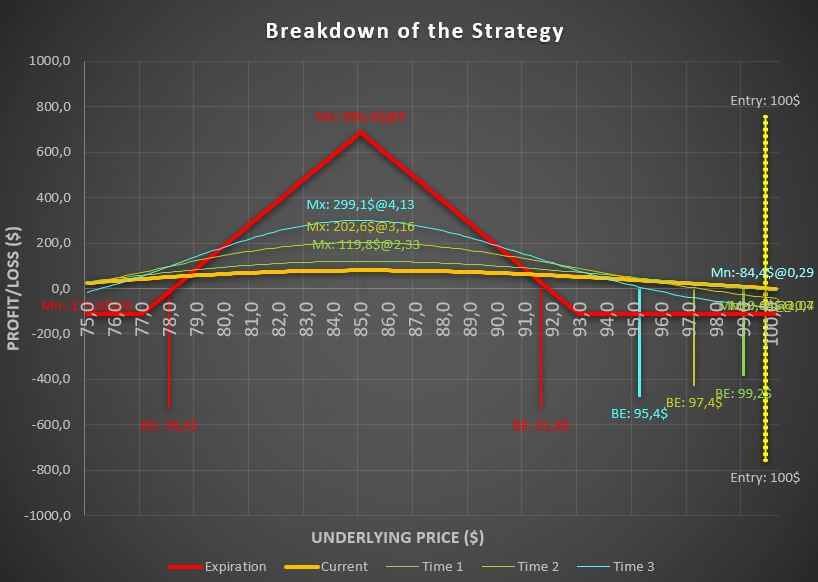
A bull put spread is a credit spread options trading strategy that involves selling a put option and buying another put option of the same underlying asset at a lower strike price.
This vertical spread allows traders to profit from a security’s upward price movement while limiting their downside risk.
Definition and Explanation of a Bull Put Spread
The process of setting up a bull put spread involves simultaneously selling a put option at a higher price and buying a put option at a lower price.
The put option sold serves to offset the cost of the put option bought, thereby lowering the overall capital requirement necessary to initiate the position.
One important note is that the options must have the same expiration date and underlying asset.
How to Set Up a Bull Put Spread
The following steps can be followed to set up a bull put spread:
- Select a security in your portfolio that you anticipate experiencing upward price movement in the near future
- Sell a put option at a strike price below the current price of the underlying security
- Buy the same number of put options at a lower price
- Ensure that both options have the same expiration date
- Collect the premium from the sold put option and apply it towards the purchase of the lower-priced put option
The Pros and Cons of Using a Bull Put Spread
Some of the benefits of using a bull put spread include the ability to profit from a stock’s upward price movement, the limited risk associated with the strategy, and the ability to receive a credit upfront from selling the put option.
However, there are also some drawbacks, such as the limited profit potential when compared to other options trading strategies and the potential loss of the premium earned if the stock price drops below the strike price of the sold put option.
Overall, a bull put spread can be a useful tool in options trading for those who are looking to limit their risk while still having the potential to earn a profit.
Comparing Bull Call Spreads and Bull Put Spreads
When it comes to options trading, two popular vertical spreads are the bull call spread and the bull put spread. Understanding the key differences between these two strategies is important for making an informed decision in options trading.
Let’s take a closer look at each one:
Key Differences Between the Two Vertical Spreads
One of the main differences between the bull call spread and the bull put spread is the direction of the market. While the former is used when a trader is bullish on an asset, the latter is used when the trader is neutral to bullish.
Additionally, the bull call spread is a debit strategy, which means it requires upfront payment, while the bull put spread is a credit spread, meaning the trader collects premium upfront.
Another key difference is the strike prices. The bull call spread involves buying a call option at a lower strike price and selling a call option at a higher strike price, while the bull put spread involves selling a put option at a higher strike price and buying a put option at a lower strike price.
Understanding Debit and Credit Spreads
As mentioned earlier, the bull call spread is a debit spread, meaning it requires an upfront payment. In contrast, the bull put spread is a credit spread, which means the trader receives an upfront premium.
Debit spreads are used when traders believe the price of the asset will increase, while credit spreads are used when traders believe the price will remain stable or increase slightly.
Analyzing Risk and Reward Ratios of the Two Strategies
Both the bull call spread and the bull put spread have defined risk and reward ratios. The risk of each strategy is limited to the amount paid or collected upfront, while the reward is limited by the difference between the strike prices of the options involved in each spread.
The reward-to-risk ratio for each strategy can vary depending on market conditions, so it’s important for traders to understand the risks and rewards involved before executing a trade.
While each strategy has its benefits and drawbacks, choosing the right one will depend on the trader’s market outlook and risk tolerance. A clear understanding of the differences between the bull call spread and the bull put spread is essential for successful options trading.
Maximizing Profit and Minimizing Risk
When it comes to options trading, maximizing profit and minimizing risk is key. Here are some strategies and tips for doing just that:
Strategies for Managing the Leg of a Vertical Spread
One way to manage the leg of a vertical spread is to adjust the strike price.
By adjusting the strike price, traders can alter the risk-reward ratio of the spread. Additionally, traders can close out the position early if they see the spread is not performing as well as expected.
This can help to minimize losses and preserve capital.
Calculating Maximum Loss and Maximum Profit
In order to maximize profit and minimize risk, it’s important to calculate the maximum loss and maximum profit for each potential trade. This can be done by using an options calculator or by hand.
Knowing the maximum loss and profit allows traders to make informed decisions and set realistic expectations for a potential trade.
Tips for Choosing the Right Vertical Spread for Any Market Condition
Choosing the right vertical spread for any market condition is an important part of maximizing profit and minimizing risk. Here are some tips for choosing the right spread:
- Consider the current market conditions and how they may impact the underlying asset
- Choose a spread with a risk-reward ratio that aligns with your trading strategy and goals
- Look for spreads with high liquidity to ensure easy entry and exit points
- Monitor the spread closely and be prepared to adjust or close out the position if necessary
By following these strategies and tips, traders can improve their chances of success and maximize their profits while minimizing risk when using vertical spreads in options trading.
Examples of Using Bull Spreads in Options Trading
Examples of using bull spreads in options trading involve different market conditions, underlying assets, and strike prices. These case studies illustrate the profitability and risk-averse nature of vertical spreads.
Case Study: Trading Options for a BioPharma Company
Trading options for a BioPharma Company requires an in-depth understanding of the industry and market forces that affect stock prices. A bullish outlook on a biotechnology company’s stock prompts the purchase of a bull call spread.
A call option with a strike price of $130 is purchased for a premium of $10, while a call option with a strike price of $140 is sold for a premium of $4.
The net cost of executing the spread is $6, which is the maximum loss for the strategy. The breakeven price for the position is $136, which is the strike price of the long call option plus the net cost of the spread.
The maximum profit for the strategy is $4, which is the difference between the strike prices of the call options minus the net cost of the spread.
Using Vertical Spreads for Managing Long-Only Options trading
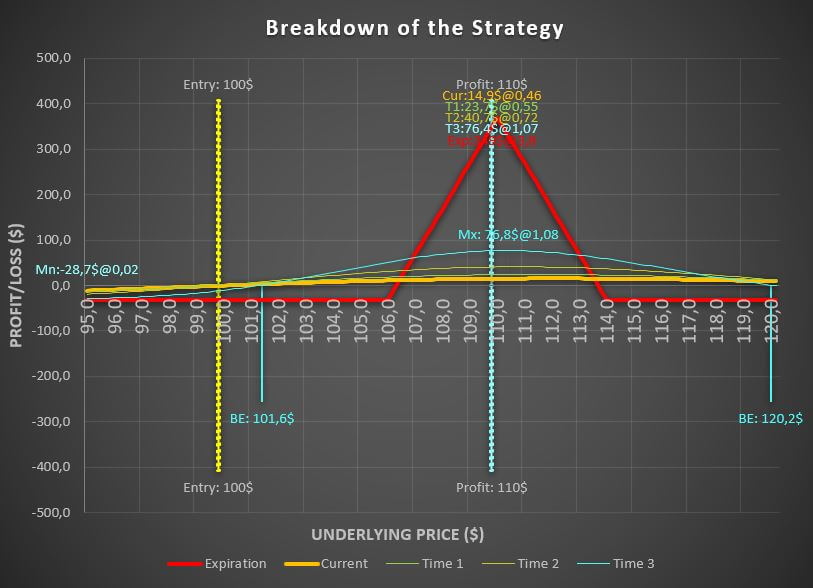
Long-only option trading involves taking long positions in the market and holding them for an extended period. Vertical spreads are an excellent tool for managing risk in this scenario. By buying a call option with a higher strike price and selling a put option with a lower strike price of the same underlying asset, traders earn a credit while defining the risk.
Since the maximum loss is the difference between the strike prices of the options minus the credit received, these spreads limit the downside while allowing for profit even if the underlying stock price does not move.
The Concept of a Bull Put Spread
The bull put spread involves selling a put option and buying another put option with the same expiry date and underlying asset at a lower strike price. The maximum profit for this strategy is limited to the net credit received, which is the difference between the premiums of the individual options.
The maximum loss for the strategy is limited to the difference between the strike prices of the options minus the net credit received. This strategy is used when the underlying asset’s price is expected to rise moderately or stay the same.
Overall, using bull spreads in options trading can be an effective way to manage risk and generate profit. Whether you are trading for a biopharma company, managing long-only options trading, or executing a bullish put spread, understanding the different vertical spreads’ nuances is key to success.
Understanding Margin Requirements for Vertical Spreads
Margin requirements play a critical role in any options trading strategy, including vertical spreads. In this section, we will explore the margin requirements for buying and selling options and how important they are in options trading.
We’ll also discuss the risks associated with trading spreads on margin.
Margin Requirements for Buying and Selling Options
Margin requirements refer to the amount of cash or securities that a trader must deposit with a broker before engaging in options trading. In the case of vertical spreads, margin requirements vary based on the type of spread and the underlying asset.
For bull call spreads, traders must have enough cash or securities in their accounts to cover the cost of buying the call option. The margin requirement for bull call spreads is typically lower than that of buying a call option outright, as the sale of the higher strike call option helps offset the cost of the lower strike call option.
On the other hand, bull put spreads require traders to have enough cash or securities in their accounts to cover the difference between the strike price of the two options.
The margin requirement for bull put spreads is generally higher than that of a bull call spread, as the sale of the lower strike put option doesn’t provide as much cushion against potential losses as the sale of the higher strike call option in a bull call spread.
The Importance of Margin in Options Trading
Margin requirements are a key consideration for traders as they determine the amount of leverage available for each trade. Trading on margin allows traders to increase their potential returns, but it also amplifies their potential losses.
As such, it’s important to have a solid understanding of margin requirements before engaging in options trading.
Moreover, margin requirements can dictate a trader’s level of risk tolerance. A higher margin requirement means that a trader must deposit more cash or securities in their account, which may be prohibitive for some traders.
On the other hand, a lower margin requirement may provide a false sense of security and encourage traders to take on more risk than they can handle.
Risks of Trading Spreads on Margin
While trading spreads on margin can increase a trader’s potential returns, it also comes with significant risks. The most significant risk is that of margin calls, which occur when a trader’s account balance falls below the margin requirement.
If this happens, the trader will be required to deposit additional cash or securities into their account to meet the margin call, or they may be forced to close out their positions at a loss.
Additionally, trading spreads on margin can amplify losses in the event that the trade moves against a trader’s expectations. As such, it’s essential to thoroughly understand the potential risks of margin trading before engaging in any options trading strategy.
Understanding margin requirements is a key component of successful trading in any options strategy, including vertical spreads. Traders need to have a solid understanding of how margin impacts their potential returns and risks, and they must be prepared to meet margin requirements at all times.
……