A bullish or bull call spread is another option spread strategy that we should consider when we do not have enough money to pay the price of the contracts we desire to buy.
In this article, we will see how does a bull call spread works. We will analyze the behavior of the bull call spread strategy, and of course, we will take a look at the bull call spread payoff diagram when the expiration date arrives.
What is a bull call debit spread strategy?
The bullish call debit spread strategy consists of a trade we perform by buying a call option contract at a certain strike price while selling another with a lower strike price.
As with the other spreads, this strategy has a limited profit and loss mechanism, so it is ideal for eliminating many of the drawbacks of selling naked options.
When to use the bull call debit spread strategy?
The bull call spread strategy is applied when we expect underlying prices to increase in value over time, within the expiration date in which we acquired the options contracts. So, in other words, this is a pure bullish position.
To help us correctly identify is the asset is going to be bullish or bearish, we highly recommend you to use some kind of trend follower, such as the supertrend technical indicator. In this way, we will make sure that the price is going to keep bullish.
The greater advantage of this strategy is that we are reducing the premium we would have to pay for the call option. However, the biggest disadvantage is we are eliminating the unlimited side of the profits that a call option would provide us.
How is the bull call debit spread composed?
The bull call debit spread strategy consists of buying a call contract with a strike price that is below the strike price of the second call contract sold.
In this way, every time we open a trade, we will be paying some money or facing a debit since the strike we buy is much more expensive than the one we sell.
This is known as a debit spread since, as we said, we are paying to open the position, just exactly as the bear call credit spread.
Bull call spread example
Let us suppose we want to open a bull call spread strategy over Alcoa Corporation, since we are quite sure aluminum prices will rise in the next few months.
Assuming that the underlying is currently valued at $15, we decide to open a bull call spread in which we will buy the call whose strike price is $14, while at the same time, we will sell the call strike value $16, both for an expiration date of 45 days.
Bull call spread calculator
Therefore, we will have to pay $113 for the bought strike, while we will receive $18 for the sold strike.
Thus, the bull call spread will result in a total debit of $95 for each of the bull call spreads that we decide to open.
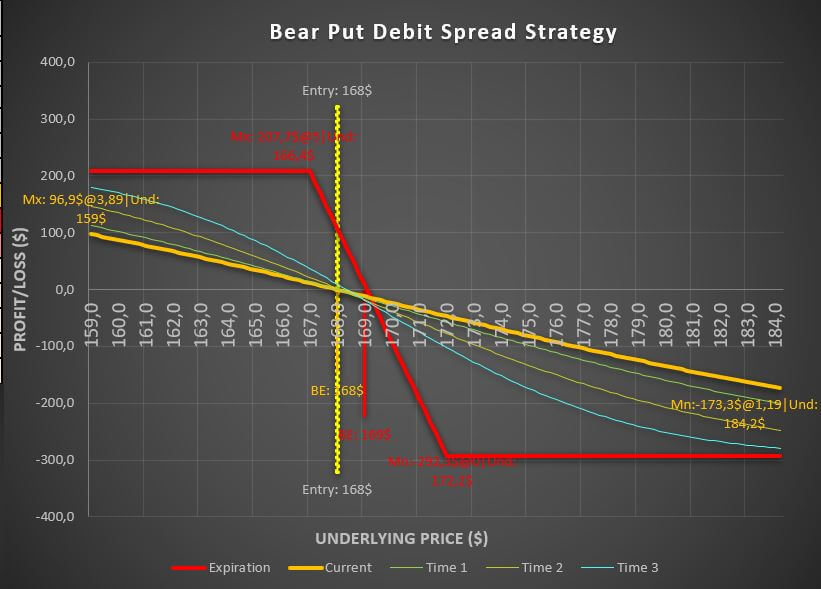
Bull call debit spread payoff diagram
In the bull call spread strategy, we will make a profit as the underlying prices increase in value while generating a loss as they fall. Since this option strategy is based on the fact that the buying option is the predominant force, the bull call spread inherits some of the buying options disadvantages, such as the negative effects of time decay.
This means that as time goes by, our position will lose value, and therefore, the profit and loss curve will be smaller and smaller. So, the expiration date, the bull call debit spread payoff diagram will look like this.
Bull call spread payoff diagram
Breking down the debit call spread
As you can see, we have two scenarios in the extremes cases.
If the underlying falls below $14 at expiration, the call bought will start to lose its value quickly, while the call sold will expire without value. Thus, the maximum loss is $98.
However, if the underlying increases above $16, no matter how much the value increases further, the gains the call bought will begin to offset the losses produced by the call sold, so we will always maintain a stable proportion and benefit, in this case, $102 at most.
However, if the underlying price falls between the two strikes of the bull call spread, we will enter the area of the curve where we could either make a profit or a loss.
Our break-even point would be obtained by adding the premium we have paid when opening the spread to the lowest strike. In other words, $14.98 is our break-even.
Bull put spread margin requirement
In this case, the worst-case scenario is that the underlying does not rise its value.
In these cases, we will lose all the money we paid when we opened the trade. And precisely because we are paying to open the bull call spread, the broker is not going to ask us any margin requirement, so we could open as many spread as we want.
In other words, we will be able to use a cash account to open this kind of strategies.
Last words about the bull call debit spread
As you can see, this strategy tries to limit the price we have to pay when buying a call option contract since it reduces it by selling another call contract at a lower price.
The big advantage of this bull strategy is that we will pay less than the simple option purchase, but its disadvantage is that we will limit our profits since the strike sold produces an additional loss covered by the strike bought.
This is one of the many other option trading strategies we can use to profit from the option market.